News
Understanding Bike Frame Geometry
Bike frame geometry is key important part while choosing bike. It helps to predict how does the bike handles, riding position and performance. It also be useful when you are planning to change a new bike frame.
Different brand bikes has different bike geometry. Hence, understanding of bike geometry will benefit you when comparing different bikes and manufacturers (brands).
Every bike frame has frame size sticker whether in numeric and alphabet. Alphabet size naming such as S / M / L / XL whereas numeric could be in inch (usually on mtb) or cm (on road / touring / cs)
To solve this puzzle, following are the key important parts of frame geometry everyone should know.
Frame size
Different bike manufacturers (brands) will name bike size in different way whether it be via alphabet like XS, S, M, etc. or in numeric measurement like 49cm, 52cm, etc. But to represent the frame size has not universal or governed by standard. Hence bike frame geometry is important for better understanding of frame size.
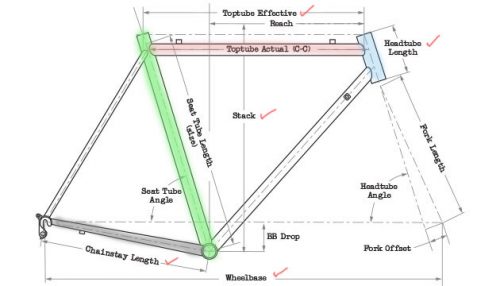
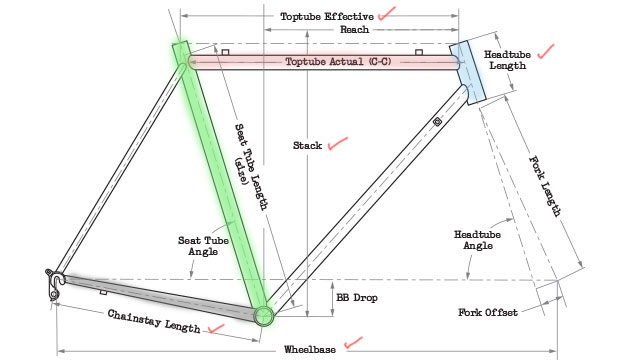
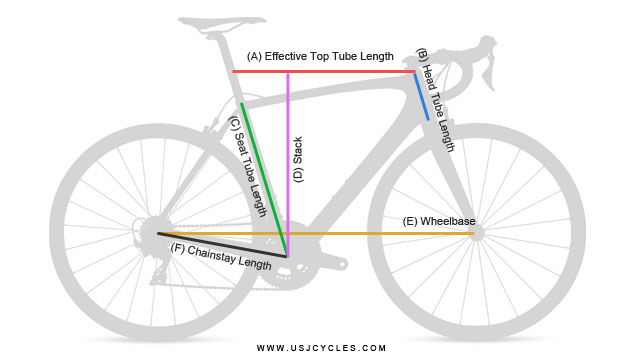
Effective Top Tube (ETT)
“Effective” top tube is referring to horizontal straight length from head tube to seatpost. This measurement is best way to determine a frame size as frame top tube sloping vary with across brands especially road bike.
Stack & Reach
We put this two terms together as it is related to Effective top tube measurement. Stack is a vertical length from center bottom bracket to top head tube. Reach is a horizontal length from bottom bracket to top head tube.
Endurance bikes (e.g. Specialized Roubaix series, Giant Defy, Cube Attain) will have longer stack and shorter reach than performance road bike (Aero/Sprint/TT) create more comfort handling. Whereas, short stack and longer reach usually applied on performance road bike such as Aero/TT/All-round road bike, result lower frontal profile to improve aerodynamics.
Head Tube Angle & Length
Angel of the head tube affect the steerer responsiveness. Steeper head tube angle create fast responsive steerer usually applied on performance MTB / Road bike so that rider can steer handle easily.
Slacker head tube usually applied on urban (Hybrid), touring bike. It create more stable and comfort of handling.
Head Tube length determine how upright riding position. You could not change the riding position much as nature of head tube serve the riding purpose. Example, comparison between endurance road bike, aero road bike, has different head tube length.
Seat Tube Angle & Length
Seat tube angle or length is not a key important part to concern unless rider would like to create a some stand over clearance usually 1-2″ from the top tube.
Wheelbase
Horizontal length from the centre to centre of front and rear wheel. Wheelbase determine the responsiveness, stability and control of the bike.
Long wheelbase – More flex and compliance. Create more comfort and stable in control in slow speed. Usually, long wheelbase geometry design on hybrid bike, touring, cross trail (Casual MTB).
Short wheelbase – Stiff and responsive in control. Usually apply in performance road bike, Time Trail (TT Bike), Aero Bike
Chainstay Length
Longer wheelbase will have longer chain stay length. It create more flex at rear wheel and less vibrations transfer to rider. Hence, it does not steer as quick as short wheelbase.
Long chain stay length applied on urban bikes, hybrid, city bike, etc
Short chain stay length usually applied on performance road bike and mtb
Geometry Comparison Endurance / All-Rounder / Aero
[wpdatatable id=326]
Based on the geometry comparison table, we can see the all-rounder frame (e.g Tarmac) has head tube length which sit between aero (e.g. Allez Sprint) and endurance (e.g. Roubaix). To create comfort and stability, endurance frame geometry has longer wheelbase and stack than the others.
*geometry comparison measurement (mm) is based 52cm size frame from Specialized Roubaix (Endurance), Tarmac (All-Rounder), Allez Sprint (Aero)
Where to get your frame bike geometry information?
Visit the official brand product specification of your bicycle.
Comfort + Stability = Endurance
Responsive Power transfer + Performance = All-rounder
Sprint + Performance = Aero / TT